Project based learning
Digital Information
Unit 1: Introduction
Unlike a traditional introduction to programming, we will try to explore many of the foundational ideas of computing so all of us understand how these concepts are transforming the world we live in.
Unit 2: Representing Information
This lesson introduces the concept of sending bits of information from one place to another. This lays the foundation for understanding how complex information is represented in computers using a combination of bits.
Unit 3 – Circle Square Patterns
Students will create rules for ordering patterns of circles and squares. Students generate all possible messages with three place values, then create rules that explain how they ordered each message.
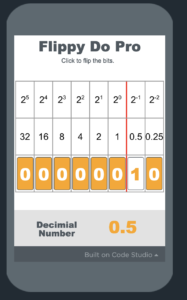
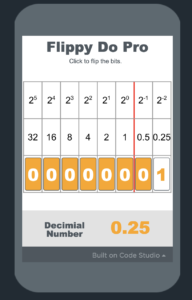
Unit 4 – Binary Numbers
In this unit, students will practice representing numbers in binary (base 2), transitioning from the circle-square representations they made in the last lesson. They will practice converting numbers and explore the concept of place value in the context of binary numbers.
Unit 5 – Overflow & Rounding
This unit introduces students to the practical aspects of using a binary system to represent numbers in a computing device. Students discover the limitations of creating numbers that are “too big” or “too small” to count
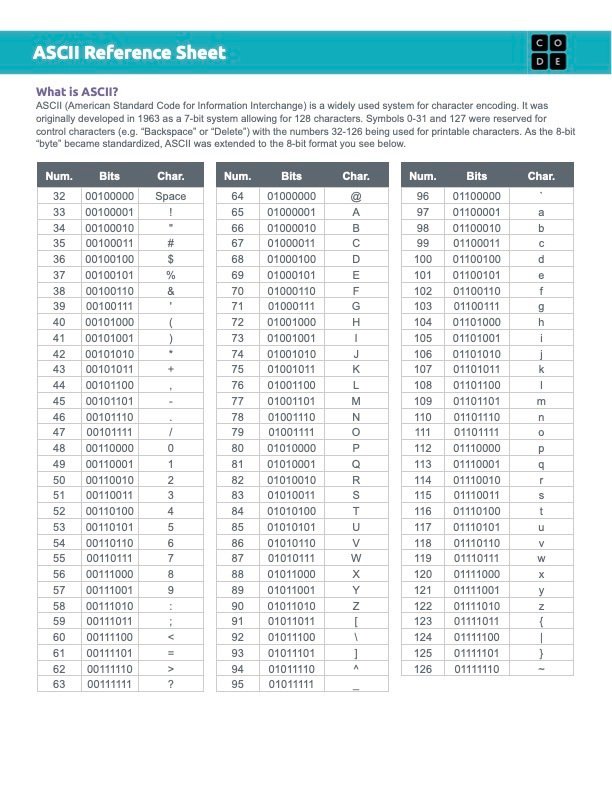
Unit 6: Representing Text
In this Unit students will understand the ways the most common types of information, text and numbers, are stored using binary.
Unit 7: Black and White Images
Throughout this unit, students gradually discover how to use bits to represent more complex data types. In this case, students work on representing images using sampling. Students quickly realize that very tiny sample squares are needed to approximate an image’s curves and small details.
Unit 8: Color Images
This Unit continues the story of how bits are used to represent digital images. Students will use the Pixelation Widget to attempt to make digital approximations of analog images, this time in color. These images are produced using layers of abstraction, with each layer relying on the other to perform its process.
Unit 9: Lossless Compression
Students use the Text Compression Widget to experiment with compressing songs and poems and try to find their ‘personal best’ compression. As a wrap-up, students discuss what factors make some texts more compressible than others.
Unit 10: Lossy Compression
Students will be able to examine the effects of lossy compression on text & images. Given a piece of media, decide whether to use lossy or lossless compression based on the needs of a situation.
Unit 11: Intellectual Property
Students have been examining how digital information is created and stored, but they have not closely examined the question of who owns their digital data and what rules govern how that information can be shared.
Unit 12: Project – Digital Information Dilemmas
In this unit students begin tackling the question of whether digitizing information has made the world a better or worse place.